Combining Form That Means Ovary
10 Female Reproductive System
- Identify the anatomy of the female reproductive system
- Describe the master functions of the female reproductive organisation
- Spell the medical terms of the female person reproductive system and utilize correct abbreviations
- Identify the medical specialties associated with the female reproductive organization
- Explore common diseases, disorders, and procedures related to the female person reproductive arrangement
Female Reproductive System Word Parts
Click on prefixes, combining forms, and suffixes to reveal a list of word parts to memorize for the female reproductive arrangement.
Introduction to the Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system produces and reproductive hormones. In addition, the female person reproductive system supports the developing fetus and delivers it to the outside world. The female person reproductive system is located primarily inside the pelvic cavity. The female gonads are called ovaries and the gamete they produce is chosen an oocyte.
Lookout man this video:
Media ten.one. Reproductive Organisation, Part 1 – Female Reproductive System: Crash Course A&P #40 [Online video]. Copyright 2015 by CrashCourse.
Female Reproductive System Medical Terms
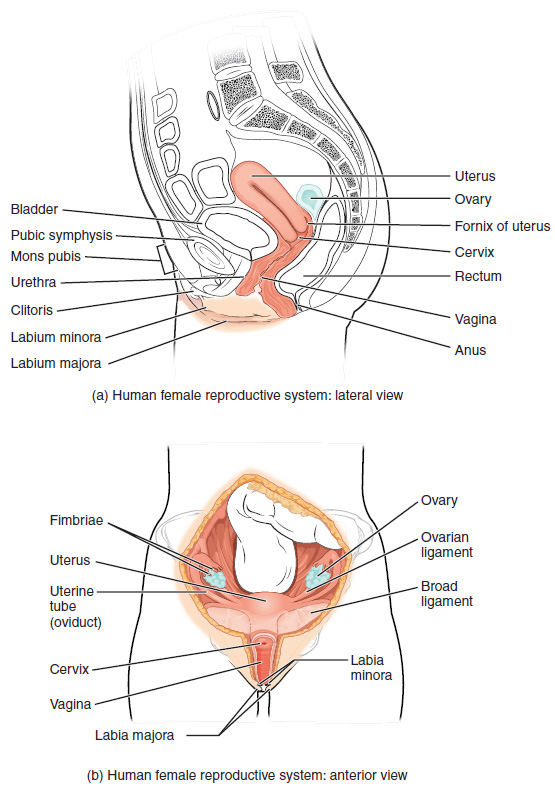
Anatomy (Structures) of the Female Reproductive Organization
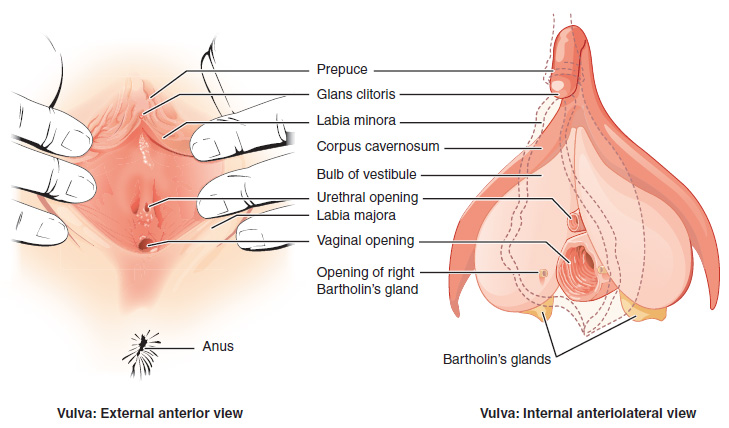
External Female person Genitals
The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively every bit the vulva and they include:
- The mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. After puberty, information technology becomes covered in pubic hair.
- The labia majora (labia = "lips"; majora = "larger") are folds of hair-covered peel that brainstorm only posterior to the mons pubis.
- The labia minora (labia = "lips"; minora = "smaller") is thinner and more pigmented and extends medially to the labia majora.
- Although they naturally vary in shape and size from woman to woman, the labia minora serve to protect the female person urethra and the entrance to the female reproductive tract.
- The superior, anterior portions of the labia minora come up together to encircle the clitoris (or glans clitoris), an organ that originates from the same cells as the glans penis and has abundant fretfulness that make it important in sexual sensation and orgasm. The hymen is a thin membrane that sometimes partially covers the entrance to the vagina.
- The vaginal opening is located betwixt the opening of the urethra and the anus. Information technology is flanked by outlets to the Bartholin'due south glands .
Internal Female person Reproductive Organs
Vagina
The vagina is a muscular canal (approximately 10 cm long) that is the entrance to the reproductive tract. It as well serves equally the leave from the uterus during catamenia and childbirth. The outer walls of the anterior and posterior vagina are columns with ridges. The superior meets the uterine cervix. The cervix is the opening to the uterus.
The walls of the vagina are lined with:
- An outer, fibrous adventitia
- A middle layer of shine musculus
- An inner mucous membrane with transverse folds called rugae .
Together, the middle and inner layers permit the expansion of the vagina to arrange intercourse and childbirth. The thin, perforated hymen can partially environment the opening to the vaginal orifice. The and the lesser vestibular glands (located near the clitoris) secrete mucus, which keeps the vestibular area moist .
The vagina has a normal population of microorganisms that help to protect against infection. In that location is both pathogenic bacteria, and yeast in the vagina. In a good for you adult female, the most predominant type of vaginal bacteria is from the genus Lactobacillus, which due southecretes lactic acrid. the lactic acid protects the vagina past maintaining an acidic pH (below 4.five).
Lactic acid, in combination with other vaginal secretions, makes the vagina a self-cleansing organ. Withal, can disrupt the normal rest of healthy microorganisms, and increase a woman'south risk for infections and irritation. Information technology is recommend that women do not douche and that they allow the vagina to maintain its normal healthy population of protective microbial flora.
Ovaries
The ovaries are the female gonads. At that place are two, one at each entrance to the fallopian tube. They are each about two to iii cm in length, virtually the size of an almond. The ovaries are located within the pelvic cavity. The ovary itself is attached to the uterus via the ovarian ligament. The ovarian stroma forms the bulk of the developed ovary. Oocytes develop within the outer layer of this stroma, each surrounded by supporting cells. This group of an oocyte and its supporting cells is called a follicle.
The Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes are the conduit of the from the ovary to the uterus. Each of the two fallopian tubes is close to, but not straight connected to, the ovary.
- The isthmus is the narrow medial stop of each uterine tube that is continued to the uterus.
- The wide distal infundibulum flares out with slender, finger-similar projections called fimbriae.
- The middle region of the tube, called the ampulla, is where fertilization oftentimes occurs.
The fallopian tubes accept three layers:
- An outer serosa
- A middle smooth muscle layer
- An inner mucosal layer
- In addition to its mucus-secreting cells, the inner mucosa contains ciliated cells that beat in the management of the uterus, producing a current that will be critical to moving the .
The Uterus and Cervix
The uterus is the muscular organ that nourishes and supports the growing embryo. Its average size is approximately five cm wide past 7 cm long and it has three sections.
- The portion of the uterus to the opening of the uterine tubes is chosen the fundus.
- The eye section of the uterus is called the torso of uterus (or corpus).
- The cervix is the narrow portion of the uterus that projects into the vagina.
- The neck produces fungus secretions that become thin and stringy under the influence of high systemic plasma estrogen concentrations, and these secretions tin can facilitate sperm motility through the reproductive tract.
The wall of the uterus is made up of three layers:
- Perimetrium: the most superficial layer and serous membrane.
- Myometrium: a thick layer of smooth musculus responsible for uterine contractions.
- Endometrium: the innermost layer containing a connective tissue lining covered past epithelial tissue that lines the lumen. It provides the site of implantation for a fertilized egg, and sheds during menstruation if no egg is fertilized.
- Write or draw out the components of the pathway that an oocyte takes from start to terminate.
- Why do you lot think the fallopian tubes are not continued to the ovaries?
Physiology (Part) of the Female person Reproductive System-Ovulation
Post-obit ovulation, the Fallopian tube receives the oocyte. Oocytes lack flagella, and therefore cannot move on their ain.
- Loftier concentrations of estrogen that occur around the time of ovulation induce contractions of the smooth muscle forth the length of the Fallopian tube.
- These contractions occur every 4 to 8 seconds, causing the oocyte to period towards the uterus, through the coordinated chirapsia of the cilia that line the outside and lumen of the length of the Fallopian tube which pulls the oocyte into the interior of the tube.
- Once inside, the muscular contractions and beating cilia move the oocyte slowly toward the uterus.
- When fertilization does occur, sperm typically encounter the egg while it is even so moving through the ampulla.
Lookout man this video:
Spotter this video on ovulation from MedLine Plus to find ovulation and its initiation in response to the release of FSH and LH from the pituitary gland.
Media ten.2. Ovulation. From Betts, et al., 2013. Licensed nether CC Past 4.0.
The Menstrual Cycle
The three phases of the menstrual cycle are:
- The menses phase of the menstrual cycle is the phase during which reproductive hormone levels are low, the woman menstruates, and the lining is shed. The period stage lasts between 2 – 7 days with an boilerplate of 5 days.
- The proliferative phase is when menstrual flow ceases and the endometrium begins to . During this phase reproductive hormones are working in to trigger ovulation on approximately day 14 of a typical 28-day menstrual cycle. Ovulation marks the finish of the proliferative phase.
- The secretory phase the endometrial lining prepares for implantation of a fertilized egg. If no pregnancy occurs within approximately 10- 12 days the endometrium volition grow thinner and shed starting the first 24-hour interval of the adjacent wheel.
Anatomy Labeling Activeness
Female Reproductive Arrangement Terms not Hands Broken into Word Parts
Female Reproductive Arrangement Medical Abbreviations
Diseases and Disorders of the Female Reproductive System
Cancer
Chest Cancer
Chest cancer starts in the cells that line the ducts or the lobule of the breast. Some alarm signs include a new lump in the breast or , thickening or swelling, irritation or dimpling of the breast peel, redness or flaky skin, pain, discharge, all in the breast or nipple area, and change in breast size. Risk factors include family history, obesity, hormonal treatment and changes in breast cancer-related genes (BRCA1 or BRCA2) (Centers for Affliction Command and Prevention, n.d.; Cancer Care Ontario, north.d.).
Handling options include chemotherapy, radiation and surgical interventions such as , biopsy, incision and drainage and (Centers for Affliction Control and Prevention, n.d.; Cancer Care Ontario, n.d.). To learn more almost chest cancer, view the Cancer Care Ontario: Breast Cancer web page.
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is typically deadening-growing cancer and is highly curable when constitute and treated early on. Advanced cervical cancer may crusade abnormal bleeding or belch from the vagina such as bleeding after sexual activity. It is diagnosed during a Papanicolaou test (or Pap smear) which looks for precancers, cell changes, on the cervix. The Pap examination can find cervical cancer early, when treatment is most effective. The Pap test only screens for cervical cancer (Centers for Illness Control and Prevention, 2019).
The HPV (Human papillomavirus) test looks for HPV strains which is the virus that can cause precancerous prison cell changes. Almost all cervical cancers are caused past HPV. HPV is a mutual virus that is passed from one person to another during sexual contact. In Canada, there is the HPV vaccine. The age of assistants varies between the provinces and territories. See below nether HPV for more information about the HPV vaccine (York Region Health Connect, n.d.). To learn more about cervical cancer please visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's cervical cancer factsheet (PDF file).
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is an abnormal condition of the . Endometriosis occurs when this tissue grows and implants exterior the uterus. The female person hormone estrogen causes these implants to grow, bleed, and break down. They are implanted exterior the uterus have no style to go out the torso. They go painful, inflamed, and swollen. The inflammation causes scar tissue around nearby organs which tin interfere with their normal functioning and cause hurting (Canadian Women'south Wellness Network, 2012).
Endometriosis generally appears between the ages of 15 and l. Signs and symptoms may include , , , menstrual irregularity and infertility. One-3rd of women diagnosed with endometriosis have no symptoms at all.Diagnosis may include and endometrial biopsy. Handling may include medication, surgical interventions such as and . The cause of endometriosis is unknown (Canadian Women's Health Network, 2012). To learn more nigh endometriosis visit the Endometriosis FAQ article on Canadian Women's Health Network.
PCOS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) has no known etiology but researchers have linked it to excessive insulin product. Excessive insulin in the body tin can release actress male person hormones in women. Since the ovaries produce high levels of this causes the eggs to develop into cysts and instead of releasing during ovulation, the cysts build up and enlarge. The nearly common symptoms of PCOS include , , , enlarged ovaries with multiple modest painless cysts or follicles that course in the ovary, , , , thinning hair, acne, weight proceeds, feet, depression, hyperglycemia, and infertility (Canadian Women's Health Network, 2012a).
Treatments like medications such as birth control pills or can assistance balance the hormones in your body and relieve some of the symptoms (Canadian Women's Wellness Network, 2012a).. To learn more most PCOS visit the PCOS article on the Canadian Women'southward Health Network.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
The terms for Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) and Sexuality Transmitted Diseases (STD) are often used interchangeably. Sexuality Transmitted Diseases (STD) implies the illness was acquired through sexual transmission. A disease is a disorder of structure or function in a man, which produces specific signs or symptoms. A affliction must be managed, equally with the case of Human being Immunodeficiency Virus (which tin can also exist acquired to through the transmission of other bodily fluids; thus not solely sexual transmission). The treatment may include or (Urology Intendance Foundation, 2019).
Chlamydia (CT)
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) caused past bacteria that infect the cervix, urethra and other reproductive organs. Chlamydia is easy to care for and tin be cured. Many people with chlamydia do non have any symptoms and unknowingly pass the infection to their sexual partner(due south). If symptoms develop, they usually appear two to half-dozen weeks afterward sexual contact with an infected person. While females are most often asymptomatic they may experience . Left untreated, chlamydia in females can lead to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) which can cause permanent damage to the reproductive organs and subsequent infertility (Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Chlamydia, 2018) (Chlamydia and Gonorrhea, n.d.).
Chlamydia spreads through unprotected oral, anal or vaginal sex with an infected person. Chlamydia tin can be spread to the eyes via the hands with direct contact of infected fluids. Until a patient finishes their treatment, they continue to have the infection and tin go along to pass information technology to others . Chlamydia is treated with antibiotic pills. If the patient has , they may need to exist hospitalized and be treated with intravenous (Four) antibiotics. All sexual partners inside the past 60 days should be examined, treated, and informed that having no symptoms does not mean there is no infection (Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion , 2019; Region of Peel, 2007).
Gonorrhea (Gonococcus) – (GC)
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria that infects the cervix, urethra and other reproductive organs. Infections can too infect the throat and anus. Gonorrhea can be treated and cured. Many people infected with Gonorrhea have no symptoms and can unknowingly pass the infection on to their sexual partner(due south). If symptoms develop, they may appear two to seven days afterwards sexual contact with an infected person. Symptoms vary depending on which part of the body is infected. Females may experience abnormal vaginal bleeding, discharge, or . Left untreated, Gonorrhea in females may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease and fertility complications such as ectopic pregnancy. Gonorrhea infection from oral sex may lead to sore throat and swollen glands. Gonorrhea infection from anal sexual practice may cause itchiness and discharge from the anus. Gonorrhea is spread through unprotected oral, vaginal or anal sex with an infected person. Until the patient finishes their treatment, they continue to take the infection and can pass it to others (Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion, 2019a; Region of Peel, 2007).
Gonorrhea is treated with oral in combination with an (IM) injection. It is of import that ane completes the handling and abjure from unprotected sex for at to the lowest degree 7 days following treatment. All sexual partners within the past 60 days should be examined, treated and informed that having no symptoms does not mean at that place is no infection (Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion, 2019a; Region of Peel, 2007).
Reportable Diseases
Both chlamydia and gonorrhea are reportable diseases to the Ministry building of Health and Long Term Intendance. Therefore, the local wellness department will exist calling the doctors office or patient to ensure correct treatment was received and sexual partners have been followed up with testing and treatment (Ontario Agency for Health Protection and Promotion, 2019a; Region of Skin, 2007). To learn more most STIs and STDs such equally chlamydia and gonorrhea delight get to the Public Health Ontario web page on sexually transmitted infections.
Human Papillomavirus- HPV
HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI). Both males and females can be infected with HPV. Almost three quarters of sexually agile individuals have been exposed to HPV during their lifetime. There are over 100 strains of HPV and some strains of HPV can cause visible genital warts. The warts are usually painless but may be itchy, uncomfortable and difficult to treat. Some strains of HPV cause genital, anal, throat and cervical cancers . HPV spreads through sexual activeness and skin-to-skin contact in the genital surface area with an infected person. Since some people are they don't know they accept the virus and consequently pass the virus to their sexual partners. Treatments are available for genital warts only there is no cure for HPV (York Region Health Connect, due north.d.).. To acquire more about HPV symptoms, treatments, and prognosis visit the York Region Fact Sheet on HPV (PDF file).
HPV Vaccine
A vaccine called Gardasil® 9 is available for nine HPV strains. This vaccine assists the immune organisation in protecting the torso against infections and diseases caused by HPV (York Region Health Connect, due north.d.). To larn more about Gardasil® 9 treatments, delight visit the Gardasil® ix website.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
Genital canker is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by a virus called canker simplex virus (HSV). There are ii types of herpes simplex viruses:
- Type 1- oral herpes or cold sores (HSV-1)
- Type 2- genital herpes (HSV-ii).
These viruses are very similar and either type tin can cause genital canker or cold sores. Symptoms might include , enlarged glands, , and fever. Once a patient is infected with HSV, the virus remains in their trunk even after the symptoms are gone and can cause recurring outbreaks. Between the outbreaks, the virus stays in their body. When the virus becomes active again, the symptoms return merely are usually less painful and heal faster. Recurring outbreaks vary from person-to-person, however they can be triggered by emotional or physical stress, exposure to sunlight, hormonal changes, poor nutrition, sexual intercourse, lack of sleep or a low allowed organization (Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, 2015).
Herpes is spread through directly contact with the sores or blisters of an infected person. Contact (and transfer of the virus) can occur from genitals-to-genitals, mouth-to-genitals or mouth-to-mouth. Herpes can too be passed to the anal surface area. Herpes spreads easily during sexual contact while symptoms are present, or just before an outbreak of symptoms. An infected person may spread herpes even when they take no symptoms; this is called shedding. I can spread the canker virus to other parts of their torso later touching the sores; . The fingers, eyes and other body areas can accidentally become infected in this way. Paw washing after touching sores and blisters is recommended to preclude spreading the virus (Ontario Ministry building of Health and Long-Term Intendance, 2015).
There is no cure for canker. Antiviral pills assist to reduce symptoms and speed the healing of blisters or sores and are prescribed by a md. Treatment of symptoms may be managed with medication for pain, bath salts, cold compresses and urinating in water may help to relieve discomfort. Continue the infected surface area clean and dry, vesture cotton underwear and loose habiliment to reduce discomfort. All sexual partner(southward) should exist informed. The simply mode to reduce the take chances of transmission of herpes is to avoid straight contact with the sores and to use condoms. Condoms will reduce only not eliminate risk as the virus can be present and shed from the skin in the genital area (Ontario Ministry building of Health and Long-Term Care, 2015).
To learn more almost the symptoms, complications, treatments and prognosis of HSV please visit the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care's Sexually Transmitted Diseases : Genital Herpes website or Public Health Ontario's Testing Index.
Female person Reproductive System Medical Abbreviations
Medical Terms in Context
Medical Specialties and Procedures related to the Female person Reproductive System
Gynecology
A is a specialist in the expanse of focusing on the diagnosis, handling, direction and prevention of diseases and disorders of the female reproductive system. Obstetrics is a specialty that provides intendance through pregnancy, labour, and . Farther subspecialties in women'southward health include contraception, reproductive , infertility, adolescent gynecology, and gynecological oncology (Canadian Medical Association, 2018). To learn more most obstetrics or gynecology please follow visit the Canadian Medical Association's Obstetrics/Gynecology Profile page (PDF file).
Hysterectomy
A is done to stage or treat female reproductive cancers, care for precancerous conditions of the cervix and some not-cancerous conditions that have not responded to other forms of treatment. There are three types of hysterectomy:
- A full hysterectomy removes both the uterus and the neck.
- A subtotal hysterectomy removes the uterus only.
- A radical hysterectomy removes uterus, neck, role of the vagina, and ligaments.
Sometimes the ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed at the same fourth dimension that a hysterectomy is washed. A salpino-oophorectomy (BSO) removes both ovaries and fallopian tubes. A salpingo-oophorectomy removes one ovary and one Fallopian tube (Canadian Cancer Society, 2020). To learn more about hysterectomy delight follow visit the Canadian Cancer Society's page on hysterectomies.
Female person Reproductive System Vocabulary
Acanthosis Nigricans
A disorder that causes darkening and thickening of the skin on the neck, groin, underarms or skin folds.
Acrochordons
Skin tags, teardrop-sized pieces of skin that tin can exist as large as raisins and are typically found in the armpits or neck area.
Amenorrhea
Absence of periods.
Androgens
Male hormones.
Antiandrogens
A group of medications that counteract the effects of male hormones.
Antibiotics
Medications that finish bacterial infections.
Antiretrovirals
Handling that works against the virus replication.
Anti-virals
Treatments that piece of work effectively against a virus.
Asymptomatic
Pertaining to without symptoms.
Autoinoculation
Self inoculation.
Axilla
The armpit.
Bartholin's glands
Also known as greater vestibular glands they are responsible to secrete mucus to keep the vestibular surface area moist.
Bilateral
Pertaining to both sides.
Douching
Washing the vagina with fluid.
Dysmenorrhea
Painful periods.
Dyspareunia
Painful intercourse.
Dysuria
Painful urination.
Endocrinology
The report of the endocrine glands and hormones.
Endometrium
The innermost layer containing a connective tissue lining covered by epithelial tissue that lines the lumen. Provides the site of implantation for a fertilized egg. Sheds during menstruation if no egg is fertilized.
Endoscopy
Process of viewing internally.
Fornix
Superior portion of the vagina.
Gametes
Haploid reproductive cells that contribute genetic material to form an offspring.
Gynecologist
Specialist in the report and handling of the female person reproductive system.
Gynecology
The study of the female reproductive system
Hirsuitism
Backlog hair all over the body.
Homeostasis
Biological process that results in stable equilibrium.
Hysterectomy
Surgical removal of the uterus.
Inferior
Pertaining to beneath.
Intramuscular
Pertaining to within the musculus.
Laparoscopy
Process of viewing internal organs.
Lumbago
Lower back pain.
Mammoplasty
Surgical repair of the chest particularly after a mastectomy.
Mastectomy
Excision of breast(s) and or breast tissue.
Oligomenorrhea
Infrequent or irregular periods.
Oocyte
Female gamete.
Oophorectomy
Surgical removal of the fallopian/uterine tubes.
Polymenorrhea
Excessive bleeding during ane's period.
Polyuria
Frequent urination.
Proliferate
Reproduce rapidly.
Puerperium
Time directly subsequently childbirth.
Superior
Pertaining to above.
Unilateral
Pertaining to one side.
Urethritis
Inflammation of the urethra.
Test Yourself
References
Canadian Medical Clan. (2018, August). Obstetrics/gynecology profile. Canadian Medical Association Specialty Proflies. https://www.cma.ca/sites/default/files/2019-01/obgyn-eastward.pdf
Canadian Women'south Health Network. (2012). Endometriosis. http://www.cwhn.ca/en/node/40779
Canadian Women's Wellness Network. (2012a). Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). http://www.cwhn.ca/en/node/44804
Cancer Care Ontario. (n.d.). Chest cancer. Ontario Health. https://www.cancercareontario.ca/en/types-of-cancer/chest-cancer
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Breast cancer: What you need to know. CDC: Cancer. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/chest/pdf/breastcancerfactsheet.pdf
Centers for Affliction Control and Prevention. (2019, January). Cervical cancer: Inside noesis virtually gynecolocic cancer. CDC: Cancer. https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/cervical/pdf/cervical_facts.pdf?src=SocialMediaToolkits
[CrashCourse]. (2015, October 2015). Reproductive organization, part i – female reproductive system: Crash grade A&P #40 [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/spotter?5=RFDatCchpus
Ontario Agency for Wellness Protection and Promotion. (2019). Chlamydia. Public Wellness Ontario. https://world wide web.publichealthontario.ca/en/diseases-and-weather condition/infectious-diseases/sexually-transmitted-infections/chlamydia
Ontario Ministry building of Wellness and Long-Term Care. (2015). Sexually transmitted diseases: Genital herpes (hur-peez). Publications. http://www.wellness.gov.on.ca/en/public/publications/std/herpes.aspx
Ontario Agency for Wellness Protection and Promotion. (2019a). Gonorrhea. Public Health Ontario. https://www.publichealthontario.ca/en/diseases-and-conditions/infectious-diseases/sexually-transmitted-infections/gonorrhea
Region of Peel. (2007). Chlamydia and Gonorrhea. https://www.peelregion.ca/health/talk-to-me/download/lesson-plans/lesson6-pdf/lesson6i.pdf
Urology Intendance Foundation. (2019). What are sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or diseases (STDs). Urology Intendance Foundation: Urologic Conditions. https://www.urologyhealth.org/urologic-atmospheric condition/sexually-transmitted-infections#Acquired_Immune_Deficiency_Syndrome_(AIDS)
York Region Wellness Connexion. (n.d.). Human papillomavirus. https://world wide web.york.ca/wps/wcm/connect/yorkpublic/b5158069-a667-4f43-bb25-e0449ba22caa/6052+Human+Papilloma+Virus+Fact+Canvass.pdf?Modern=AJPERES&CACHEID=b5158069-a667-4f43-bb25-e0449ba22caa
Image Descriptions
Figure 10.1 prototype description: This figure shows the structure and the unlike organs in the female person reproductive system. The height panel shows the lateral view with labels (clockwise from top): utuerus, ovary, formix of uterus, neck, rectum, vagina, anus, labium majora, labium minora, clitoris, urethra, mons pubis, pybic symphysis, bladder; and the bottom panel shows the anterior view with labels (clockwise from top): ovary, ovarian ligament, wide ligament, labia minora, labia majora, vagina, neck, uterine tube, usterus, fimbriae. [Render to Figure x.1].
Figure x.2 image description: This figure shows the parts of the vulva. The correct console shows the external inductive view and the left panel shows the internal anteriolateral view. The major parts are labeled (from pinnacle): prepuce, glans clitoris, labia minora, corpus cavernosum, seedling of vestibule, urethral opening, labia majora, vaginal opening, opening of right Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's glands, anus. [Return to Figure 10.2].
Unless otherwise indicated, this chapter contains material adjusted from Anatomy and Physiology (on OpenStax), by Betts, et al. and is used under a a CC Past 4.0 international license. Download and access this volume for free at https://openstax.org/books/anatomy-and-physiology/pages/i-introduction.
Combining Form That Means Ovary,
Source: https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/medicalterminology/chapter/female-reproductive-system/
Posted by: wrightsagessay.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Combining Form That Means Ovary"
Post a Comment